JS
The beginning
JavaScript is to programming what jazz is to music
~ Markus Persson
Markus Alexej Persson, known by the pseudonym Notch, is a Swedish video game programmer and designer. He is the creator of Minecraft, which is the best-selling video game in history. He founded the video game development company Mojang Studios in 2009. Persson began developing video games at an early age.
The World's Most Misunderstood Programming Language Has Become the World's Most Popular Programming Language.
~ Douglas Crockford
Douglas Crockford is an American computer programmer who is involved in the development of the JavaScript language. He specified the data format JSON, and has developed various JavaScript related tools such as the static code analyzer JSLint and minifier JSMin.

![]() Netscape
Netscape
Brendan Eich
Founder of Brave, Mozilla
Creator of JavaScript (1995)
![]()

![]()
JavaScript / ECMAScript
JavaScript was invented by Brendan Eich in 1995.
It was developed for Netscape 2, and became the ECMA-262 standard in 1997.
JavaScript / ECMAScript
After Netscape handed JavaScript over to ECMA, the Mozilla foundation continued to develop JavaScript for the Firefox browser. Mozilla's latest version was 1.8.5. (Identical to ES5)
🤡 MicroSoft 1996-1997
Microsoft reverse-engineered JavaScript and called it <JScript/>
Introduced it in 💩 Internet Explorer 3
And created two similar but not identical languages 🤯 caused browser chaos till June 15, 2022 when IE died. 🙌
1999–2008: 🫥 The Dark Ages
ES2 and ES3 … 😩
Browsers were inconsistent 🤯, devs relied on hacks and jQuery to deal with differences
September 2008
Google created V8 for its Chrome browser, and both were first released in 2008. The lead developer of V8 was 🥸 Lars Bak, and it was named after the powerful car engine.
September 2008
For several years, Chrome was 🚀 faster than other browsers at executing JavaScript.
It compiled JS to machine code using JIT
🪄 Parses it (turns it into a structure the engine can understand)
🛠️ Compiles it to machine code (not just bytecode or interpreted—this is fast, native code)
🚀 Optimizes the code at runtime (using techniques like inline caching and just-in-time compilation).
2009 ECMAScript 5 (ES5)
Big update 🤟
strict mode
Object.defineProperty
JSON support
Became widely adopted and laid the foundation for modern JS
Object.defineProperty(obj, prop, descriptor)
----------------------------------------------
const object = {};
Object.defineProperty(object, "clarity", {
value: 42,
writable: false,
});
object.clarity = 77; //// Throws an error in strict mode
console.log(object.clarity);// Expected output: 42
🚀 ECMAScript 6 (ES6 / ES2015)
Another update 👊
let and const
Arrow functions () => {}
(import/export)
Promises
🤔 arrow vs functions
An arrow function expression is a compact alternative to a traditional function expression, with some semantic differences and deliberate limitations in usage
Arrow functions don't have their own bindings to this, arguments, or super, and should not be used as methods.
Arrow functions cannot be used as constructors. Calling them with new throws a TypeError. They also don't have access to the new.target keyword.
function test () {
console.log(arguments)
}
test("ddd")
/*
Arguments ['ddd', callee: ƒ, Symbol(Symbol.iterator): ƒ]
0:"ddd",
callee: ƒ test()
length:1
Symbol(Symbol.iterator)
[[Prototype]]: Object
*/
Context caching
const myObject = {
name: 'Alex',
printAsync: function(){
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(this.name)
},1000)
}
}
Context caching
const myObject = {
name: 'Alex',
printAsync: function(){
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(this.name)
},1000)
}
}
var myObject = {
name: "Alex",
printAsync: function printAsync() {
var _this = this;
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(_this.name);
}, 1000);
}
};
var myObject = {
name: "Alex",
printAsync: function printAsync() {
var _this = this;
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(_this.name);
}, 1000);
}
};
🚀 ECMAScript 6 (ES6 / ES2015)
Template literals
Destructuring
Default parameters
⏳ Post-ES6 Era (2016–Today)
👷🏻 Yearly updates
async/await
Optional chaining (?.)
Nullish coalescing (??)
BigInt, Array.flat(), Object.entries(), Object.groupBy()... etc
Top-level await
😎 JavaScript Today
✅ Runs everywhere: browsers, servers (Node.js), desktops (Electron), mobile (React Native)
✅ Powers most modern web apps (React, Angular, Vue)
✅ Competes with many languages but remains the king of the web 👑
🏎️
The engine
🧵 Single-Threaded
😱 What Does That Mean?
🚩 One call stack
JS has one call stack, meaning it can do one thing at a time.
🚩 No multi-threading (like in C++ or Java)
so it executes code line-by-line, top to bottom.
🤌
But wait...
🧠 How does it do stuff like:
🔥 Asynchronous code
🔗 Fetching data from an API?
🕒 Waiting 5 seconds with setTimeout?
🧑💻 Responding to user clicks?
...etc
🔄 The Event Loop
JavaScript works with the help of its environment (like the browser or Node.js), and the event loop manages how asynchronous operations are handled.

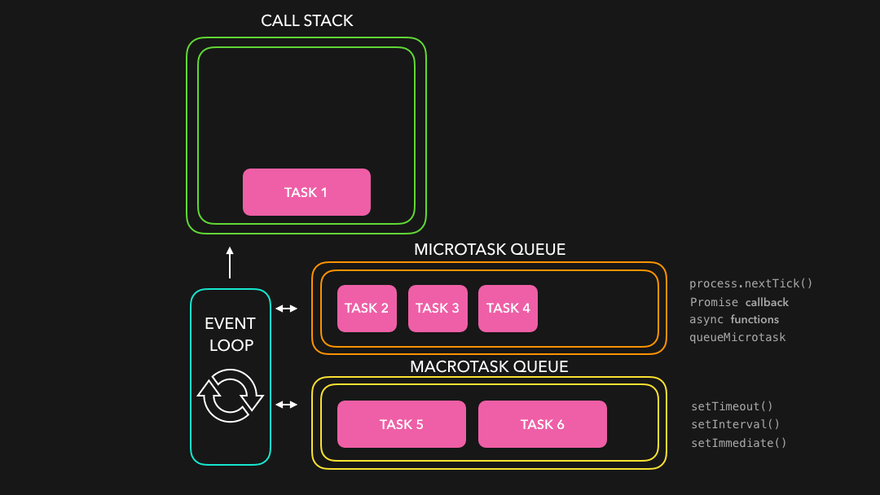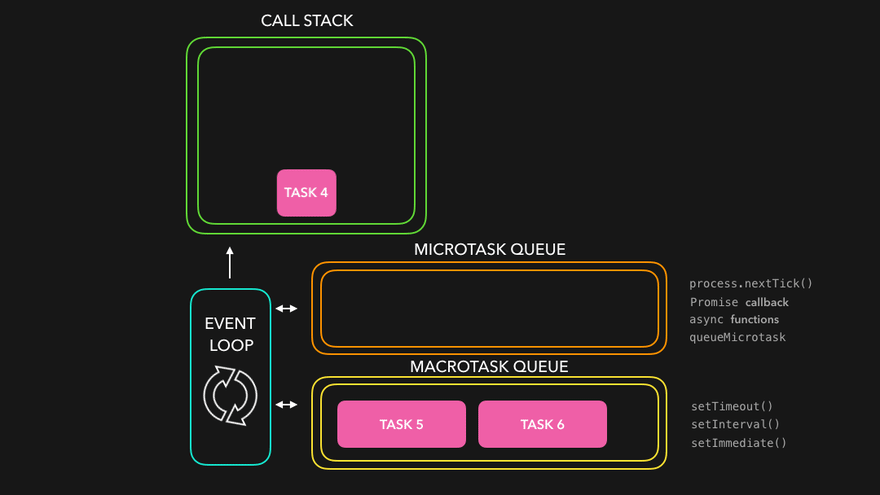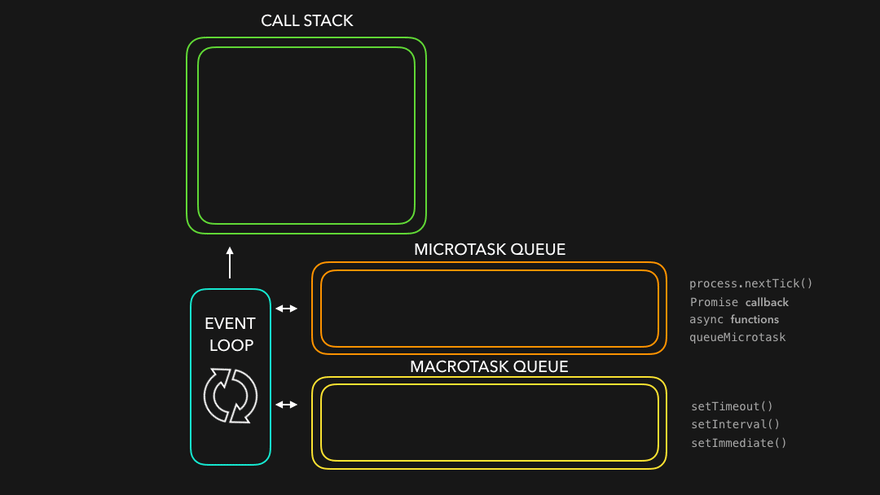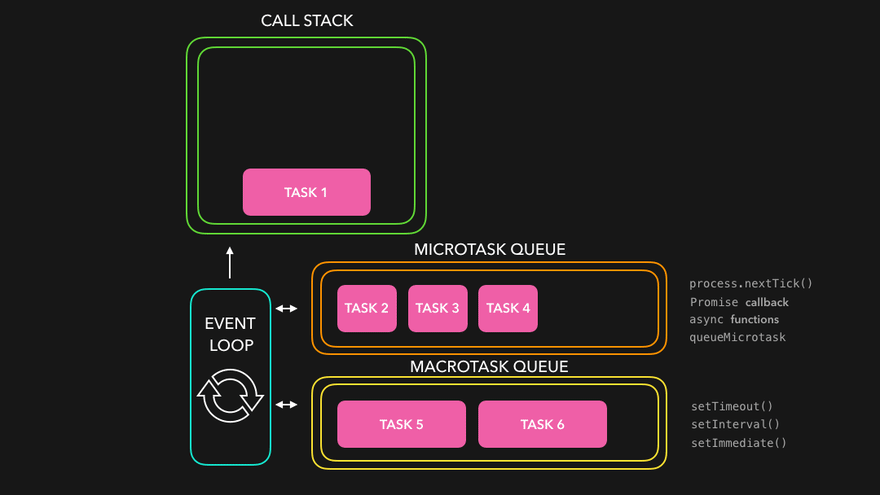
🐢
Microtasks vs Macrotasks

🧪 Microtasks
(higher priority)
Promise.then()
catch
finally
queueMicrotask
🧠 What is queueMicrotask()?
queueMicrotask(callback) schedules the callback to run at the end of the current JavaScript execution context, but before the next event loop tick.
In simpler terms, it puts the task in the microtask queue, which is processed immediately
after the current
function finishes and before any setTimeout, setInterval, or I/O events.
It's similar to Promise.resolve().then(...), but more direct and
slightly faster..
Pure Functions
A Pure Function is a function (a block of code) that always returns the same result if the same arguments are passed.
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
console.log(add(2, 3));
console.log(add(2, 3));
Memoization
In computing, memoization or memoisation is an optimization technique used primarily to speed up computer programs by storing the results of expensive function calls to pure functions and returning the cached result when the same inputs occur again.
Memoization
const foo = (x) => {
console.log("very long calculation of x")
return x * 2;
}
const memoize = function (f) {
const cache = {};
return function (x) {
return cache[x] ? cache[x] : cache[x] = f(x)
}
}
Memoization
const memoizedFoo = memoize(foo);
const res1 = memoizedFoo(42) // 84
// very long calculation of x
// cache = {}
const res2 = memoizedFoo(42) // 84
// cache = { 42: 84 }
<CustomElement onData={...}/>
customElement.prototype.getData = function (url) {
if (this.cache[url]) {
this.data = this.cache[url];
this.dispatchEvent(new Event("load"));
} else {
fetch(url)
.then((result) => result.arrayBuffer())
.then((data) => {
this.cache[url] = data;
this.data = data;
this.dispatchEvent(new Event("load"));
});
}
};
element.addEventListener("load", () => console.log("Loaded data"));
console.log("Fetching data…");
element.getData("ht tp://example.com/data.bin");
console.log("Data fetched");
First run
customElement.prototype.getData = function (url) { if (this.cache[url]) { this.data = this.cache[url]; this.dispatchEvent(new Event("load")); } else { fetch(url) .then((result) => result.arrayBuffer()) .then((data) => { this.cache[url] = data; this.data = data; this.dispatchEvent(new Event("load")); }); } };Fetching data…
Data fetched
Loaded data
customElement.prototype.getData = function (url) { if (this.cache[url]) { this.data = this.cache[url]; this.dispatchEvent(new Event("load")); } else { fetch(url) .then((result) => result.arrayBuffer()) .then((data) => { this.cache[url] = data; this.data = data; this.dispatchEvent(new Event("load")); }); } };Fetching data…
Loaded data
Data fetched
customElement.prototype.getData = function (url) {
if (this.cache[url]) {
this.data = this.cache[url];
this.dispatchEvent(new Event("load"));
} else {
fetch(url)
.then((result) => result.arrayBuffer())
.then((data) => {
this.cache[url] = data;
this.data = data;
this.dispatchEvent(new Event("load"));
});
}
};
customElement.prototype.getData = function (url) {
if (this.cache[url]) {
return this.data = this.cache[url];
} else {
return fetch(url)
.then((result) => result.arrayBuffer())
.then((data) => {
this.cache[url] = data;
this.data = data;
});
}
};
customElement.prototype.getData = function (url) {
if (this.cache[url]) {
return this.data = this.cache[url];
} else {
return fetch(url)
.then((result) => result.arrayBuffer())
.then((data) => {
this.cache[url] = data;
this.data = data;
});
}
};
const f1 = () => Promise.resolve(42)
const f2 = () => 42
f1()
// Promise {: 42}
f2()
// 42
await Promise.resolve(f1())
await Promise.resolve(f2())
//42
//42
customElement.prototype.getData = function (url) {
if (this.cache[url]) {
this.data = this.cache[url];
this.dispatchEvent(new Event("load"));
} else {
fetch(url)
.then((result) => result.arrayBuffer())
.then((data) => {
this.cache[url] = data;
this.data = data;
this.dispatchEvent(new Event("load"));
});
}
};
element.addEventListener("load", () => console.log("Loaded data"));
console.log("Fetching data…");
element.getData();
console.log("Data fetched");
customElement.prototype.getData = function (url) { if (this.cache[url]) { this.data = this.cache[url]; this.dispatchEvent(new Event("load")); } else { fetch(url) .then((result) => result.arrayBuffer()) .then((data) => { this.cache[url] = data; this.data = data; this.dispatchEvent(new Event("load")); }); } };Fetching data…
Loaded data
Data fetched
customElement.prototype.getData = function (url) { if (this.cache[url]) { this.data = this.cache[url]; this.dispatchEvent(new Event("load")); } else { fetch(url) .then((result) => result.arrayBuffer()) .then((data) => { this.cache[url] = data; this.data = data; this.dispatchEvent(new Event("load")); }); } };Fetching data…
Data fetched
Loaded data
customElement.prototype.getData = function (url) { if (this.cache[url]) { queueMicrotask(() => { this.data = this.cache[url]; this.dispatchEvent(new Event("load")); }); } else { fetch(url) .then((result) => result.arrayBuffer()) .then((data) => { this.cache[url] = data; this.data = data; this.dispatchEvent(new Event("load")); }); } };Fetching data…
Loaded data
Data fetched

🧪 Microtasks (higher priority)
- Promise.then(), catch, finally
- queueMicrotask
🕐 Macrotasks (lower priority)
- setTimeout, setInterval
- DOM events
console.log(" 👷🏻 console ")
setTimeout(() => console.log(" 🕐 setTimeout "), 0)
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log(" 🧵 Promise "))
console.log(" 👷🏻 console2 ")
console.log(" 👷🏻 console ")
setTimeout(() => console.log(" 🕐 setTimeout "), 0)
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log(" 🧵 Promise "))
console.log(" 👷🏻 console2 ")
/// 👷🏻 console
/// 👷🏻 console2
/// 🧵 Promise
/// 🕐 setTimeout
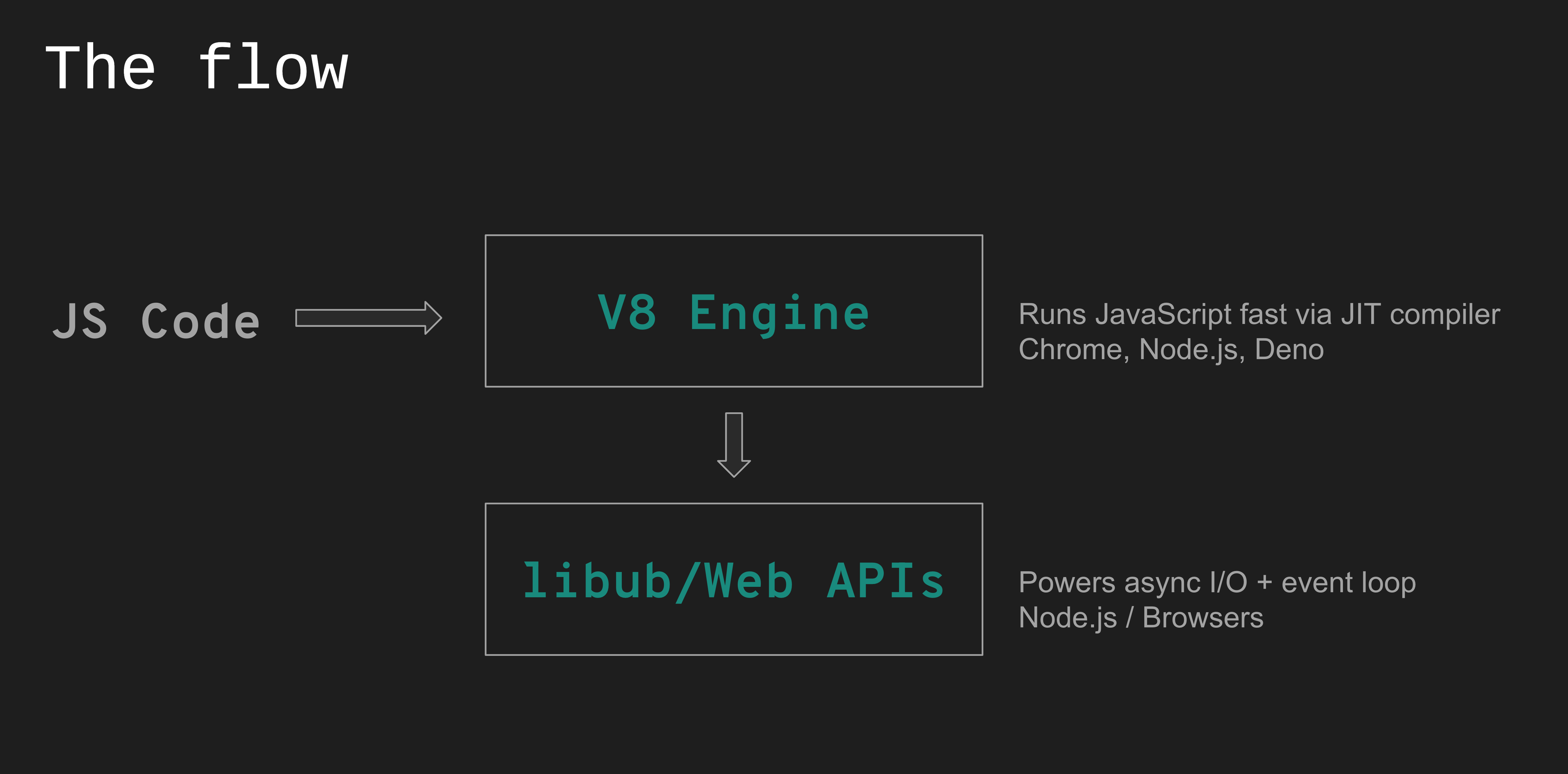
JS vs Node.js
JS runs in browser with V8 + Web APIs
Node.js runs JS in server with V8 + libuv for async ops
| Feature | JS | Node |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Runs in the browser | Runs on the server |
| Engine | V8 ( libuv like WebAPI) | V8 + libuv (for I/O) |
| Macro tasks | setTimeout, setInterval, setImmediate* | Same, plus setImmediate |
| Micro tasks | Promise.then, MutationObserver | Promise.then, process.nextTick |
| APIs | DOM, Web APIs (fetch, event handlers) | fs, http, etc. (via libuv) |
| Queue | Managed by the browser | Managed by libuv + internal Node scheduler |
| Layer | Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
| JS Engine | V8 (Chrome), SpiderMonkey (Firefox), JavaScriptCore (Safari) | Executes your JavaScript code |
| Browser Engine | Blink (Chrome), Gecko (Firefox), WebKit (Safari) | Handles DOM, rendering, layout, and event loop |
| Event Loop | Built into the browser engine | Orchestrates tasks, callbacks, and events |
| Async APIs | Web APIs (DOM timers, Fetch, etc.) | Expose async behavior to JS — implemented in C++ or Rust (libuv like) |

May the <F=ma> be with You
🧱 JS Types
JavaScript Types (as of ECMAScript 2023)
JS has two main categories of types
🧱 JS Types
Primitive: string, number, boolean, null, undefined, bigint, symbol
Reference: object, array, function, date, map, set
Type Coercion
" 5" + 1="51"
"5" - 1 = 4